Avoid N+1 Queries in Rails: Best Practices for Optimized Performance
To avoid the N+1 query problem in Rails, you need to minimize database queries that result in multiple individual queries for each record, which can slow down performance. Here’s how to prevent N+1 queries and when to apply these techniques:
0/ Setup model
# == Schema Information
#
# Table name: profiles
#
# id :bigint not null, primary key
# display_name :string
# phone :string
# created_at :datetime not null
# updated_at :datetime not null
# household_id :bigint
# user_id :string
#
class Profile < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :household, optional: true
has_many :owned_households, class_name: 'Household', foreign_key: 'owner_id'
end
# == Schema Information
#
# Table name: households
#
# id :bigint not null, primary key
# address :string
# invite_code :string
# name :string
# created_at :datetime not null
# updated_at :datetime not null
# owner_id :bigint
#
class Household < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :owner, class_name: 'Profile', foreign_key: 'owner_id', optional: true
has_many :profiles
end
1/ Eager loading – includes
- Can avoid N+1
- Rails will retrieve all required data in one or two queries instead of querying for each record separately.
- Can not use SQL on the associate table (
households) by default. But it possible withreferences()- if use
symbol, it’s association name, in this case, it:owned_households - if use
'string', it’s the table name.
- if use
- Use
includeswhen you need to load associated records to avoid multiple queries. - Rails will retrieve all required data in one or two queries instead of querying for each record separately.
When to use: When you know you’ll need associated records for a large collection.
# Let’s count the number of households owned by the profile
Profile.includes(:owned_households).map {|p| p.owned_households.size }
# Let’s add condition and check if it works or not
Profile.includes(:owned_households).where('households.id IN (1,4)')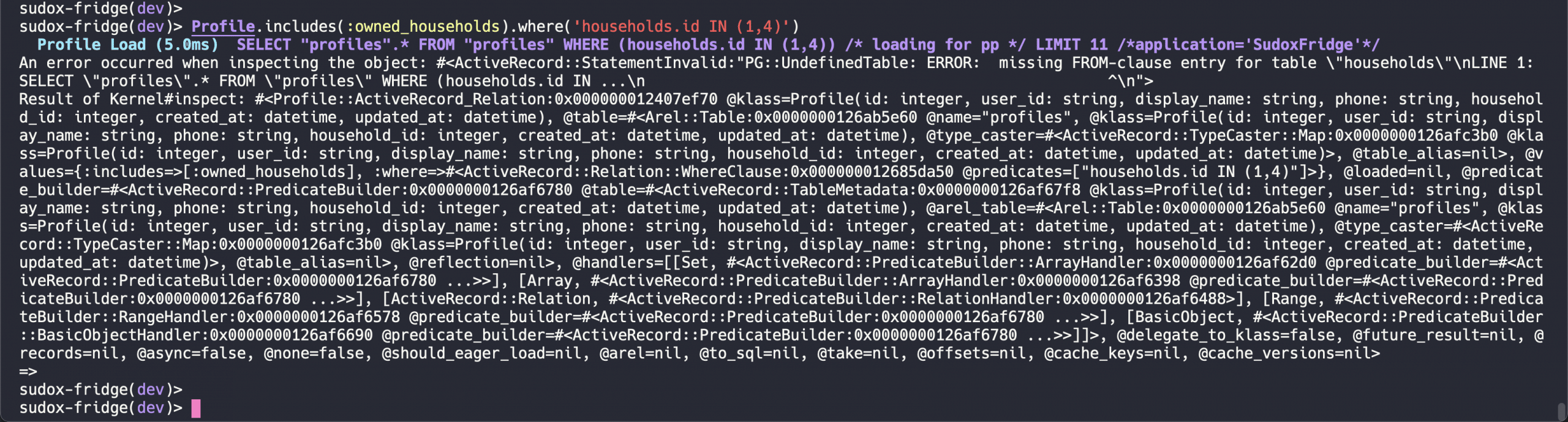
# Let’s use references
- The query looks like
eager_load, use SQL andLEFT OUTER JOIN
Profile.includes(:owned_households).where('households.id IN (1,4)').references(:owned_households).map {|p| p.owned_households.size }
2/ Preloading – preload
- Can avoid N+1
- Always generate separate queries.
- Can not use
whereonhouseholds, even if it hasreferencesor not.
Profile.preload(:owned_households).map {|p| p.owned_households.size }
3/ eager_load
- Can avoid N+1
- Convert to SQL, use
LEFT OUTER JOIN - Can use SQL on the associate table.
Profile.eager_load(:owned_households).where('households.id IN (1,2,3,4)').map{|profile| profile.owned_households.size }
4/ joins
- Can NOT avoid N+1, but we can use it with
selectorincludes - Use INNER JOIN
- Can use SQL on the associate table
joinsperforms an SQL JOIN and loads associated data in one query, but it doesn’t return the associated records.- Use
joinswhen you need to filter or sort records based on associated data but don’t need to retrieve the associated records.
When to use: When you’re querying based on the associated table but don’t need to access its data later.
Profile.joins(:owned_households).where('households.id IN (1,2,3,4)').map{|profile| profile.owned_households.size }
5/ Using select with joins or includes
- You can combine
selectwithjoinsorincludesto only fetch specific columns you need, avoiding loading unnecessary data.
When to use: When you want to minimize the data loaded from the database for performance reasons.
Profile.joins(:owned_households).select('households.id as h_id, households.name as h_name, profiles.id as p_id, profiles.display_name')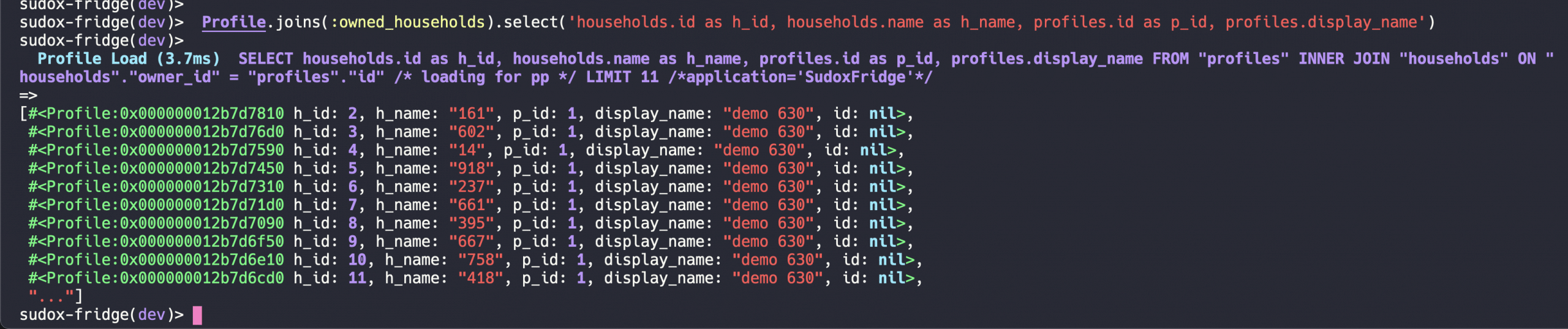
Profile.joins(:owned_households).where('households.id IN (1,2,3,4)').includes(:owned_households).map{|profile| profile.owned_households.size }
#generate household name
Profile.joins(:owned_households).where('households.id IN (1,2,3,4)')
.select('profiles.id, households.id as house_id , households.name as house_name,profiles.display_name as owner_name')
.map{|r| "house_id: #{r.house_id} - name: #{r.house_name} belongs to #{r.owner_name}"}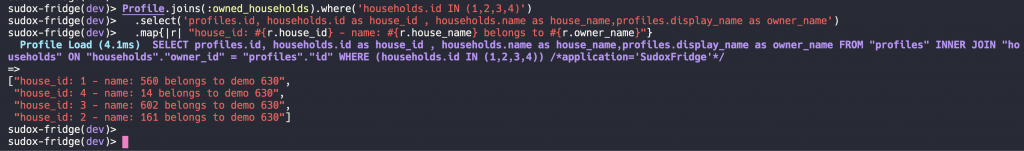
Some test code:
Profile.preload(:owned_households).map {|p| p.owned_households.length } # separate query
Profile.preload(:owned_households).where('households.id IN (1,2,3,4)')
Profile.includes(:owned_households).map {|p| p.display_name }
Profile.includes(:owned_households).where('households.id IN (1,4)').references(:owned_households).map {|p| p.owned_households.length } # separate query
Profile.joins(:owned_households).where('households.id IN (1,2,3,4)').map{|profile| profile.owned_households.size } # innter join
Profile.eager_load(:owned_households).map {|p| p.display_name} # left outer join, can use where condition on joined table
Profile.eager_load(:owned_households).map{|profile| profile.owned_households.size } # left outer join, can use where condition on joined table
Profile.eager_load(:owned_households).where('households.id IN (1,2,3,4)').map{|profile| profile.owned_households.size } # left outer join, can use where condition on joined table